In the dynamic landscape of digital marketing, where every click and conversion holds immense value, A/B testing emerges as a crucial tool for optimizing campaigns and maximizing returns. This beginner’s guide will delve into the essentials of A/B testing, providing a comprehensive overview of its principles, methodologies, and practical applications in digital campaigns. Whether you’re a seasoned marketer seeking to refine your strategies or a novice just beginning to explore the world of data-driven optimization, understanding A/B testing is paramount to achieving success in the competitive digital arena. Learn how to effectively leverage A/B testing to unlock the full potential of your digital campaigns and drive impactful results.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to design, execute, and analyze A/B tests effectively. We’ll cover key concepts such as hypothesis formulation, variable selection, sample size determination, and statistical significance. Through practical examples and real-world case studies, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of how A/B testing can be applied to various elements of a digital campaign, including headlines, calls-to-action, images, landing pages, and email marketing. By the end of this guide, you will be well-versed in the core principles of A/B testing and empowered to implement it strategically to improve your campaign performance and achieve your marketing objectives.
What Is A/B Testing?
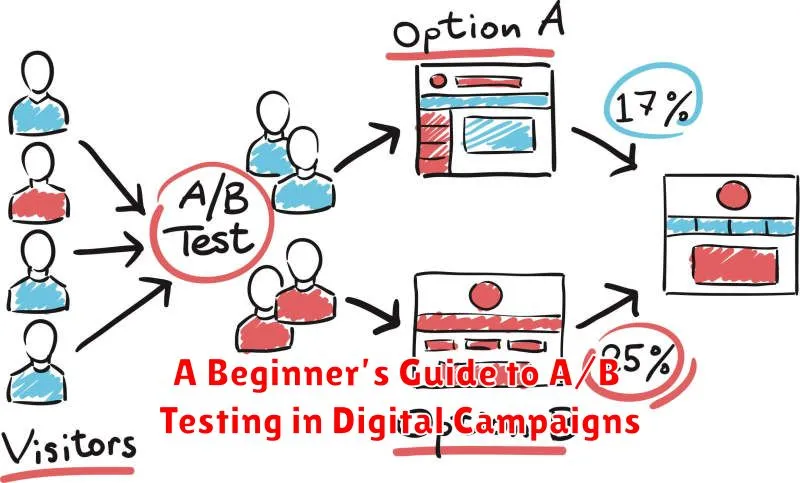
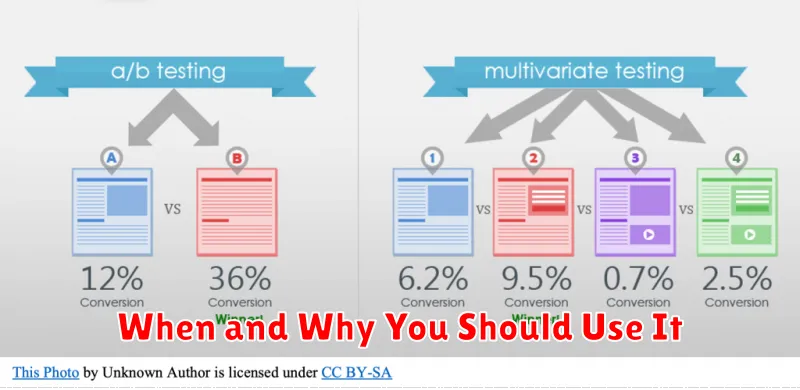
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a method of comparing two versions of something to see which performs better. Version A is the original, acting as the control. Version B is modified in some specific way.
The versions are presented to users simultaneously. Performance is measured by a chosen metric, such as click-through rate or conversion rate. The version with the statistically significant better performance is declared the winner.
When and Why You Should Use It
A/B testing is a valuable tool throughout a digital campaign’s lifecycle, not just at the beginning. Employ it when you need to make data-driven decisions about changes to your campaign elements.
Use A/B testing to optimize various aspects, such as ad copy, visuals, landing pages, and even target audience segments. This allows you to identify which version performs best based on metrics like conversion rates, click-through rates, and bounce rates.
Consider A/B testing when you want to improve campaign performance, increase ROI, and gain valuable insights into user behavior. It’s a powerful method to continuously refine your campaign and maximize its effectiveness.
Tools to Set Up A/B Tests
Several tools facilitate A/B testing implementation and analysis. Choosing the right one depends on your specific needs and budget.
Google Optimize is a popular choice, seamlessly integrating with Google Analytics. It offers a visual editor and advanced targeting options.
Optimizely is another robust platform providing comprehensive A/B testing capabilities, including multivariate testing and personalization features.
VWO (Visual Website Optimizer) offers a user-friendly interface and various testing options, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.
For simpler A/B tests, some content management systems (CMS) and email marketing platforms have built-in A/B testing features.
Choosing the Right Variables
A/B testing hinges on selecting the right variables to manipulate. Focusing on elements with the greatest potential impact yields the most insightful results. Consider testing variables tied directly to user engagement and conversion.
Some examples include call-to-action text, button color, headline phrasing, and image choices. Prioritize variables based on your campaign goals and website analytics. Avoid testing too many variables simultaneously as this can muddy the results.
Understanding Statistical Significance
Statistical significance is a critical concept in A/B testing. It helps determine if the observed differences between your A and B groups are likely due to a real change, or just random chance.
A common threshold for statistical significance is a p-value of 0.05 or less. This means there’s only a 5% chance the results you observed would have occurred if there was no real difference between your variations.
Reaching statistical significance gives you confidence that your changes are actually impacting user behavior, allowing for data-driven decisions.
Analyzing Test Results Effectively
Analyzing A/B test results requires a data-driven approach. Focus on key metrics relevant to your campaign goals, such as conversion rates, click-through rates, or bounce rates.
Use statistical significance to determine if observed differences between variations are likely due to the changes made, not random chance. A commonly used threshold is a 95% confidence level. This signifies a high probability that the observed results are real and not due to random fluctuations.
A/B Testing in Email Marketing
A/B testing in email marketing involves sending two slightly different versions of an email to two separate segments of your subscriber list. You then analyze which version performs better based on key metrics.
Key elements you can test include subject lines, email copy, calls to action, and sending times. By analyzing the results, you can optimize future campaigns for higher open rates, click-through rates, and conversions.
A/B testing allows you to make data-driven decisions, ensuring your emails resonate with your target audience and achieve your marketing objectives.
Improving Landing Page Conversion
A/B testing is a powerful tool for optimizing landing page conversions. By creating two versions (A and B) of a landing page with a single element changed, you can measure the impact of that change on user behavior.
Typical A/B test elements include headlines, call-to-action buttons, form fields, and page layout. Analyzing the resulting data helps determine which version performs better, leading to higher conversion rates.
Creating a Testing Calendar
A testing calendar provides structure and organization to your A/B testing process. It helps ensure consistent testing and prevents conflicts with other marketing activities.
Key elements of a testing calendar include the test hypothesis, the target audience, the test duration, and the metrics you’ll use to measure success. This organized approach helps in prioritizing tests and tracking progress.
A simple spreadsheet can serve as an effective testing calendar. Consider dedicating columns for each of these essential components. Regularly review and update your calendar based on past test results and evolving campaign objectives.
Common A/B Testing Pitfalls
A/B testing, while powerful, isn’t without its challenges. Falling into common pitfalls can skew your results and lead to incorrect conclusions. One frequent mistake is testing too many elements simultaneously. This makes it difficult to isolate the impact of individual changes.
Another pitfall is insufficient sample size. Testing with too few participants can lead to statistically insignificant results. Finally, be wary of prematurely ending tests. Allowing tests to run their full course ensures you gather enough data for reliable insights.